Archaeological Research & Mitigation
Our highly experienced team provide comprehensive archaeological investigation services, including survey, evaluation, watching brief, and excavation
ARCHAEOLOGICAL RESEARCH & MITIGATION
Project Planning
& Research
We have experience of designing and setting up archaeological investigations of all scales.


ARCHAEOLOGICAL RESEARCH & MITIGATION
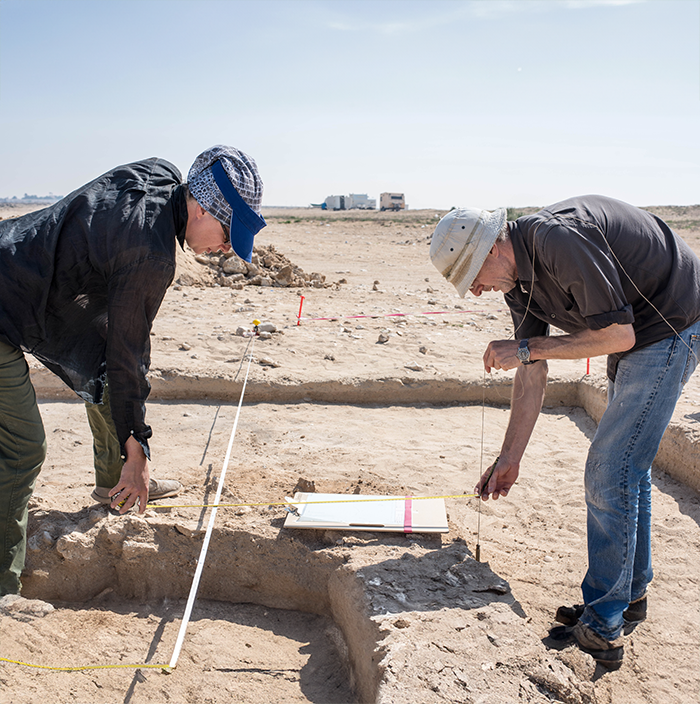
Archaeological Evaluation
An Archaeological Evaluation usually consists of trial trenching, the results of which determine the level of archaeological survival and whether there is a need for more detailed investigation.
ARCHAEOLOGICAL RESEARCH & MITIGATION
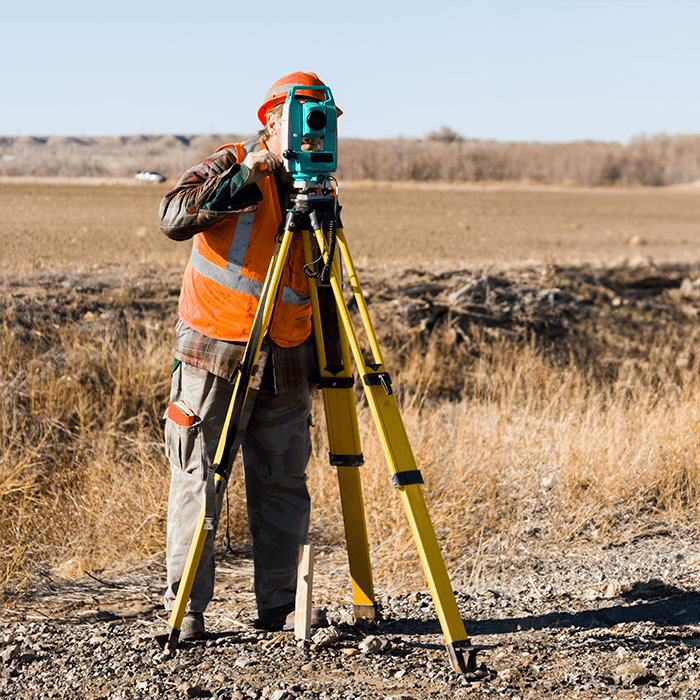
Archaeological Survey
An Archaeological Survey is a systematic process of locating, documenting, and evaluating archaeological sites or archaeological potential in a specific area.


ARCHAEOLOGICAL RESEARCH & MITIGATION
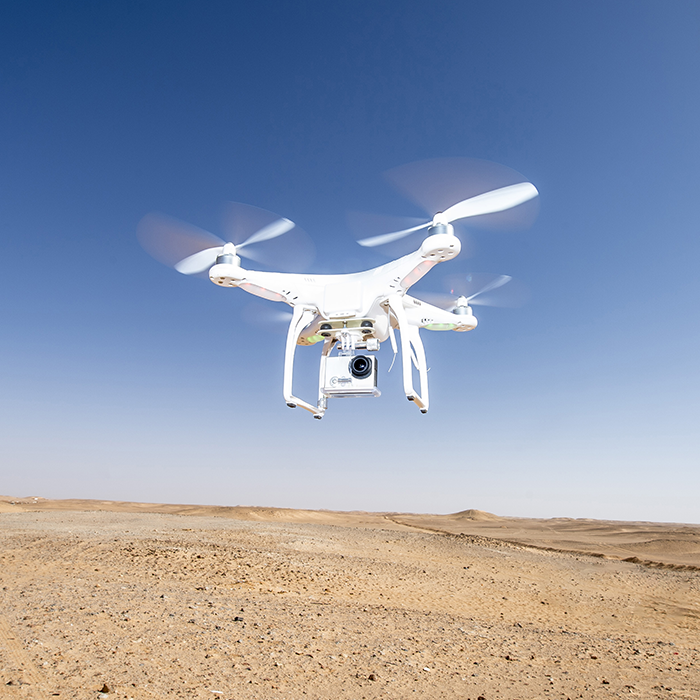
Aerial Survey & UAV Drone Survey
Features that are not visible on the ground often become visible when viewed from the air.
ARCHAEOLOGICAL RESEARCH & MITIGATION
Archaeological Watching Brief
An archaeological Watching Brief is usually undertaken to monitor groundworks on sites where there is either a history of or likelihood of archaeological remains.
Working in conjunction with developers invasive ground works (such as foundation or utility trenching) are monitored to ensure any archaeology present is fully recorded.
If significant remains are encountered further archaeological investigation and recording may be required.

ARCHAEOLOGICAL RESEARCH & MITIGATION
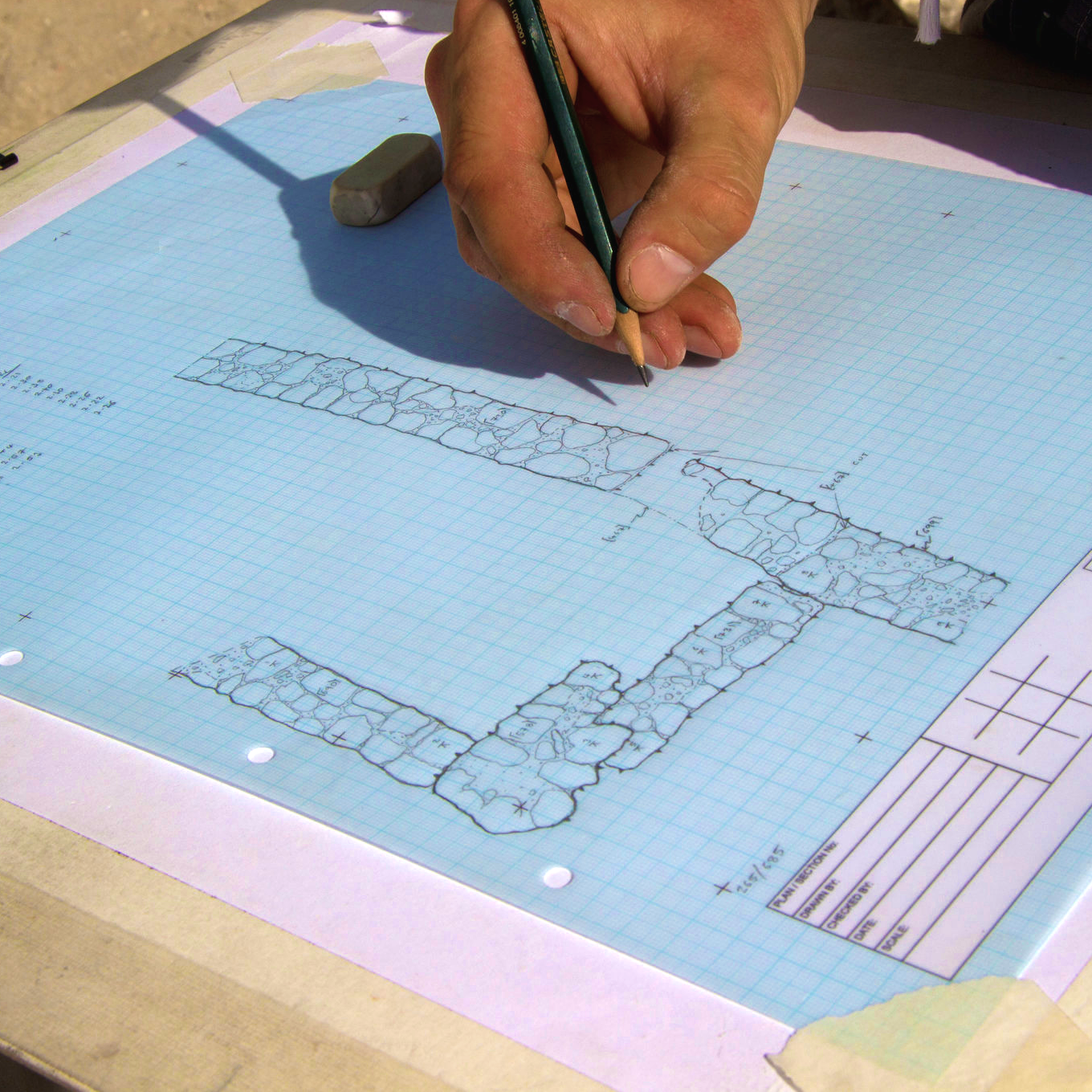
Archaeological Excavation
Archaeological Excavation can be undertaken for research or to mitigate for a development project, by recording and removing archaeological deposits (preservation my record).
Within a development setting excavation is likely to be required where the archaeological remains are of such significance that a programme of detailed investigation and recording of buried deposits is required.
ARCHAEOLOGICAL RESEARCH & MITIGATION
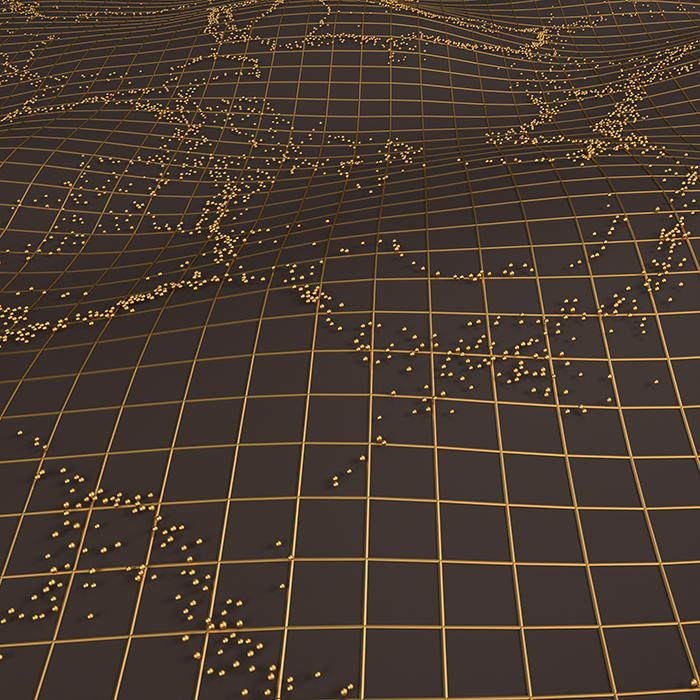
Geophysical Survey
Our geophysical survey service provides a rapid, non-intrusive method for detecting potential sub-surface archaeology.

ARCHAEOLOGICAL RESEARCH & MITIGATION
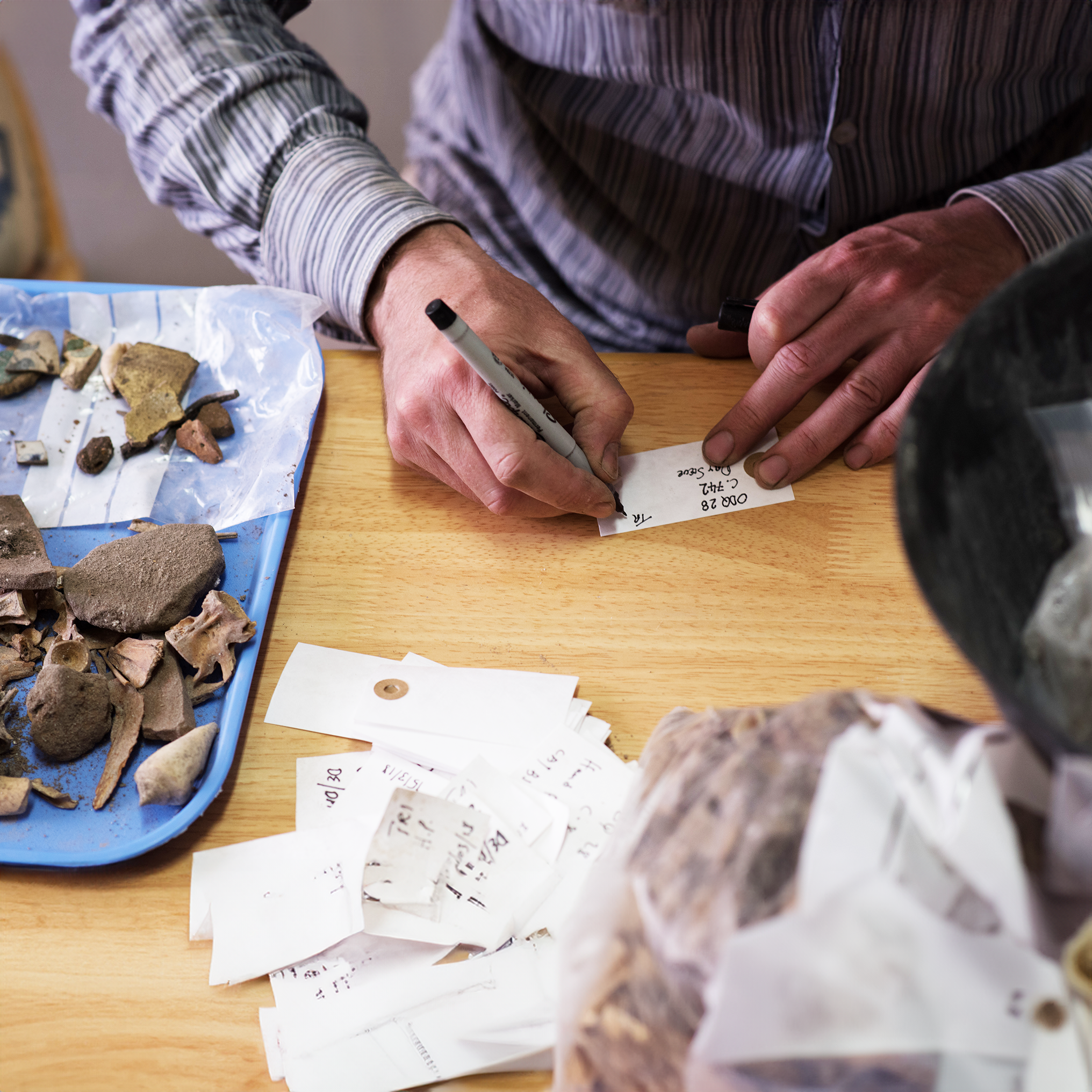
Post-Excavation Analysis & Recording
Post-Excavation is the process of analysis, cataloguing and interpretation of all the artefactual, environmental, and stratigraphic evidence collected during archaeological fieldwork.
Post excavation work uses a range of analytical and scientific techniques to answer questions such as date, form, function, and provenance of archaeological material. All such works are consistent with international professional standards and respective scientific specialisms. We deliver high quality post-excavation reporting and publication and have a proven track record of work in the region.
